The connection between diet and mental health has become a growing focus of research in both nutrition science and psychology. Food provides the body with essential nutrients that influence brain chemistry, hormonal balance, and overall cognitive function.
Diet is usually linked to physical health, but it is becoming more and more clear that it also affects mental health, emotional stability, and resiliency. Learning about this connection can help you figure out how long-term healthy eating habits may be good for your mental health.
The brain requires a steady supply of nutrients to perform at its best. Glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids form the building blocks for neural communication, while vitamins and minerals act as catalysts in biochemical processes. These nutrients play a critical role in producing neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid, all of which influence mood and cognitive performance.
An inadequate intake of essential nutrients can lead to imbalances in these chemical messengers, potentially affecting mood regulation. Diets high in processed foods, excessive sugars, and unhealthy fats may contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress, impairing both brain function and mental stability. Conversely, nutrient-dense foods help maintain optimal brain signaling and support emotional balance.
Micronutrients are indispensable for mental well-being. B vitamins, especially B6, B12, and folate, are vital for neurotransmitter synthesis and energy metabolism in the brain. Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, and low mood.
Minerals also have a significant role. Magnesium supports stress regulation by influencing the nervous system’s response to cortisol, zinc assists in neural signaling, and iron ensures adequate oxygen supply to brain tissues. A consistent and balanced intake of these micronutrients not only sustains physical energy but also reinforces mental clarity and resilience.
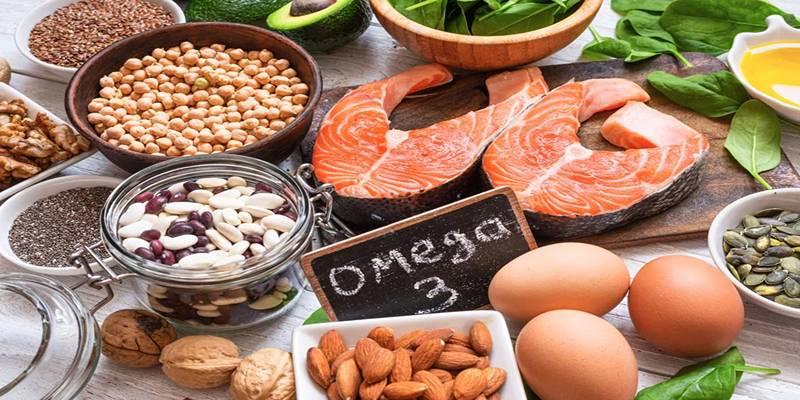

Omega-3 fatty acids—particularly EPA and DHA—are essential components of brain cell membranes. They contribute to cell fluidity, enhance communication between neurons, and possess anti-inflammatory properties. Adequate omega-3 intake has been associated with improved mood regulation and a reduced risk of depressive symptoms.
When omega-3 levels are insufficient, the efficiency of brain signaling can decline, and inflammatory responses may increase. Including omega-3-rich foods in regular meals supports not only cognitive function but also the capacity to cope with emotional challenges.
The brain relies heavily on glucose for energy. However, sharp fluctuations in blood sugar levels can influence mood, attention span, and overall mental alertness. Diets dominated by refined carbohydrates and sugars cause rapid spikes in glucose, followed by abrupt drops, which can contribute to irritability, anxiety, and fatigue.
Balanced meals that combine complex carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats help moderate glucose release, maintaining steady energy levels and more consistent mood states throughout the day. This stability supports mental focus and reduces the likelihood of stress-related mood swings.
The relationship between digestive health and mental well-being is increasingly recognized as significant. The gut houses trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiome, which play a role in nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mood regulation.
Through the gut-brain axis—a communication pathway linking the digestive system with the central nervous system—changes in gut health can influence emotional states. A diverse microbiome, supported by fiber-rich foods and fermented products, can encourage the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin. Poor dietary habits, in contrast, may disrupt this balance, contributing to inflammation and potential mood disturbances.
Long-term dietary habits influence mental wellness. Diets abundant in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and healthy fats offer a wide range of antioxidants, fiber, and anti-inflammatory compounds. Such dietary patterns have been associated with a lower risk of depression and anxiety.
On the other hand, regular consumption of highly processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive saturated fats correlates with higher rates of mood disorders. Adjusting dietary patterns toward nutrient-rich foods can provide the brain with consistent fuel and protect it from nutritional deficiencies that affect emotional health.
Water plays a crucial role in nearly all bodily functions, including those of the brain. Even mild dehydration can reduce concentration, impair short-term memory, and heighten irritability. Proper hydration supports the transport of nutrients to brain cells and the removal of metabolic waste, both of which are essential for maintaining mental sharpness.
Adequate fluid intake throughout the day is a simple yet often overlooked factor in supporting mood stability and cognitive performance. It includes water-rich foods such as fruits and vegetables, which contribute to daily hydration needs.
Diet is a significant component of mental health, but it functions best when integrated into a balanced lifestyle. Physical activity, adequate sleep, and effective stress management amplify the benefits of good nutrition. Without these complementary factors, even a nutrient-rich diet may not achieve its full potential in supporting mental resilience.
A holistic approach that combines dietary balance with healthy daily routines creates a strong foundation for both psychological and physical well-being. This integrated model aligns with the growing recognition that multiple interdependent factors shape mental health.
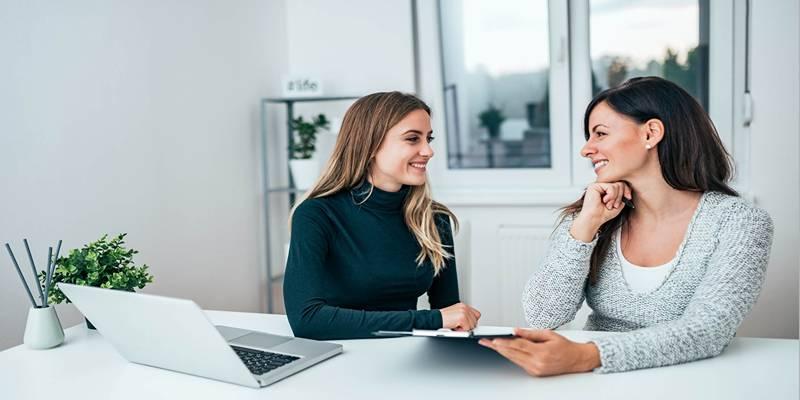

Qualified healthcare providers should assess changes in mood, persistent fatigue, or cognitive difficulties. In some cases, dietary adjustments can play a role in improving symptoms, but they may need to be combined with other medical or psychological interventions.
Registered dietitians and mental health professionals can help determine whether nutritional factors are contributing to symptoms and create tailored plans that address both physical and emotional needs. It ensures that dietary strategies are safe, effective, and appropriate for individual circumstances.
The relationship between diet and mental health reflects a complex interaction of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Nutrient-dense foods supply the brain with the resources it needs for optimal function, emotional balance, and resilience against stress. Adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, omega-3 fatty acids, and hydration supports cognitive clarity and stable mood regulation.
While diet alone is not a cure for mental health disorders, it can serve as a vital part of a comprehensive approach to psychological well-being.

Discover how hostels make budget travel affordable, social, and unforgettable.

Discover smart and easy ways to explore your dream destinations on a budget.

Explore top travel destinations blending culture, nature, and sustainability.

Balanced nutrition supports brain health and mood. Discover how diet affects emotional well-being and mental resilience.
Laser eye surgery guide detailing types, risks, recovery process, candidacy factors, and costs for improved vision.

Discover 10 science-backed strategies to optimise health, enhance wellness, and maintain long-term vitality naturally.
A 40-year study reveals that weight loss surgery lowers early death risk, offering long-term health and survival benefits.

Busy parents can enjoy the holidays with quick, healthy meals that save time, reduce stress, and support family wellness.

Learn the types, causes, and treatments for headaches, and discover when it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.

Is it safe to travel to Sicily after Mount Etna’s eruption? Here’s the latest safety advice, alerts, and travel tips for visitors

Bangkok, Lima, Lyon, Wellington, Osaka, and Lucknow are the top food capitals of the world that serve you the best local flavors

Get updated travel safety tips and real-time alerts for Bali tourists following the recent volcano eruption and ash disruptions